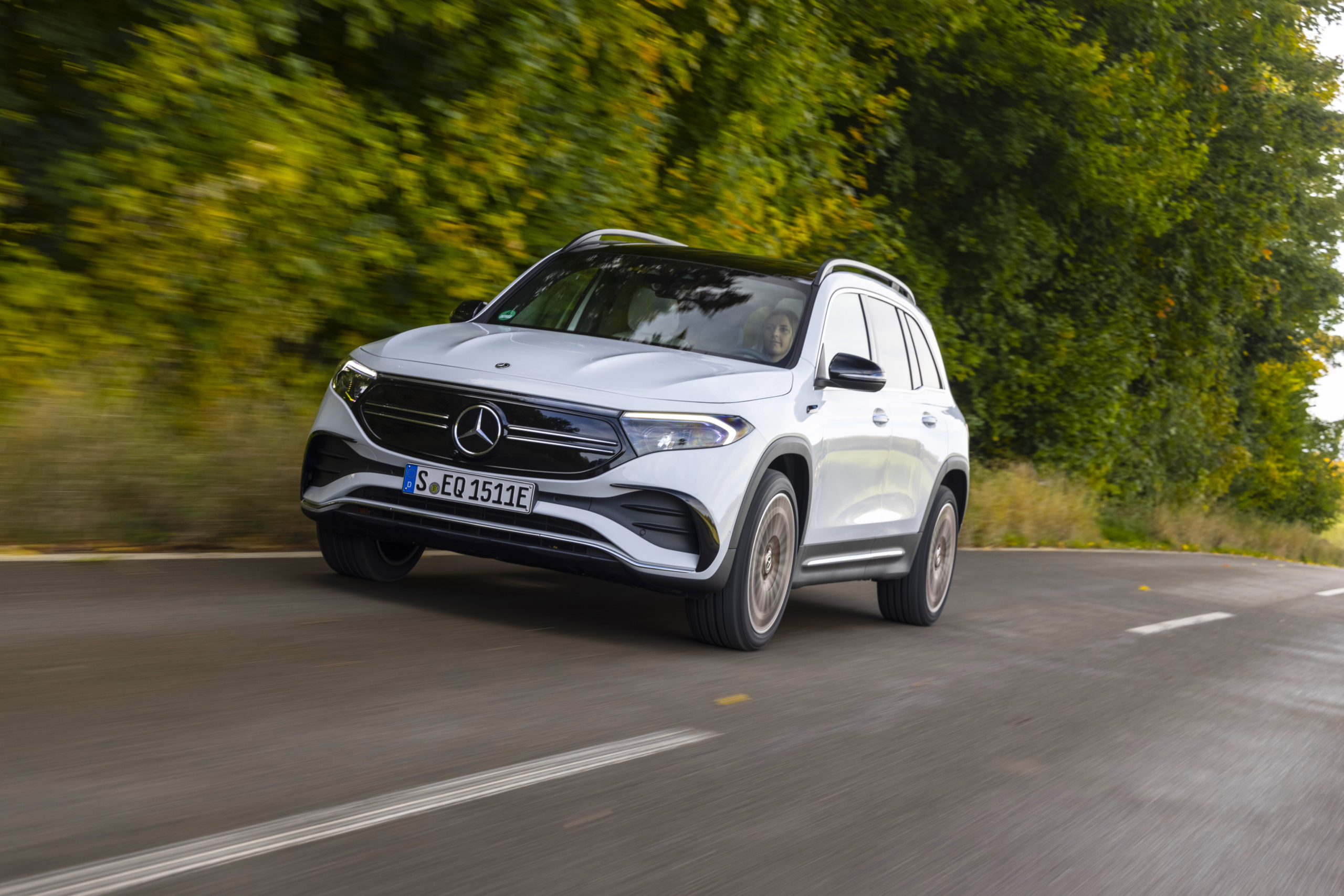
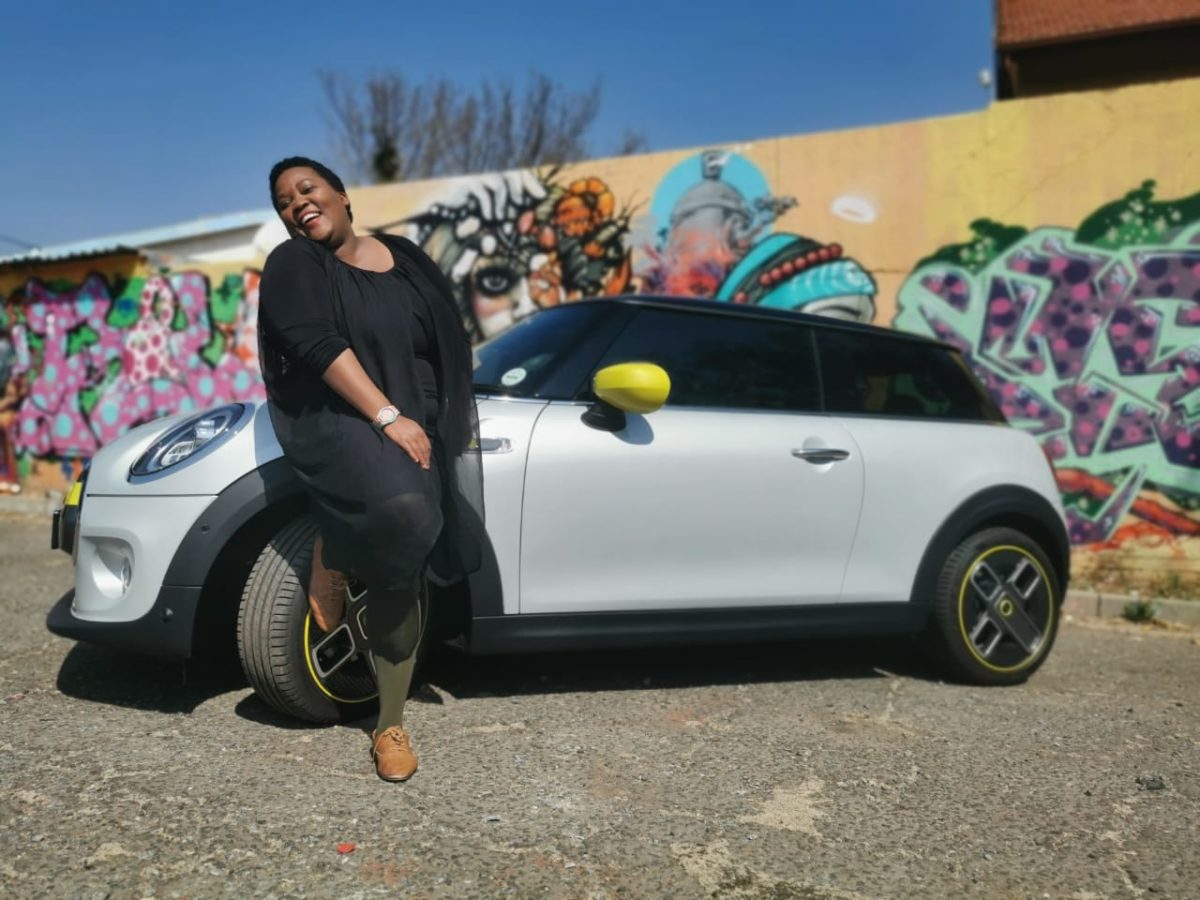
My interview with Hailey took place in the plush visitors area of their environmentally friendly dealership – MINI Midrand.
-songo didiza, Green Mobility Guru, Driving In Heels South Africa
I was invited by the PR team at MINI South Africa to review their first ever electric car – the MINI Cooper SE.
Having spent most of the national lockdown in my sneakers I wanted to grace the momentous occasion with a cross between a formal business look and environmentally fashionable dress sense. I would be meeting Hailey Philander, Specialist: Product Communications (BMW i, BMW Motorrad and MINI) for the first time and as they say, first impressions count!
My interview with Hailey took place in the plush visitors area of their environmentally friendly dealership – MINI Midrand. Over a welcome mug of cappuccino, Hailey shared that the BMW Group has already lowered emissions per vehicle produced by more than 70 percent since 2006. Their next goal is to decrease emissions by a further 80 percent by 2030.
After discussing their other long-term strategic plans, which include introducing zero emission vehicles by year 2030 it was time for me to put the MINI Cooper SE to the Heels & Horsepower Magazine’s Green Mobility Test.
As much as I am a perfectionist for practicality, I am also a staunch advocate of ‘fashionable’ green mobility
songo didiza, Green Mobility Guru, Driving In Heels South Africa
First impressions
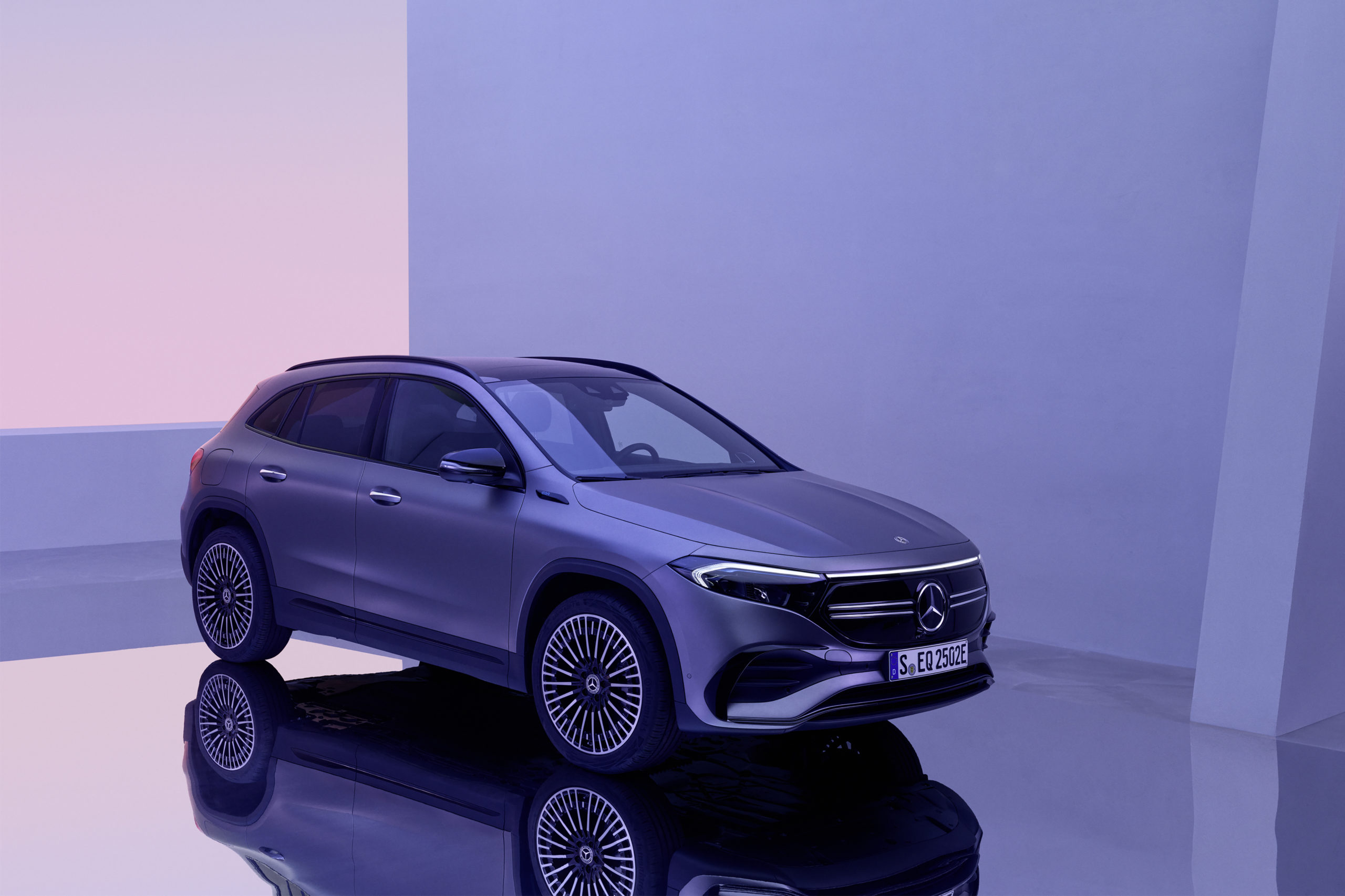
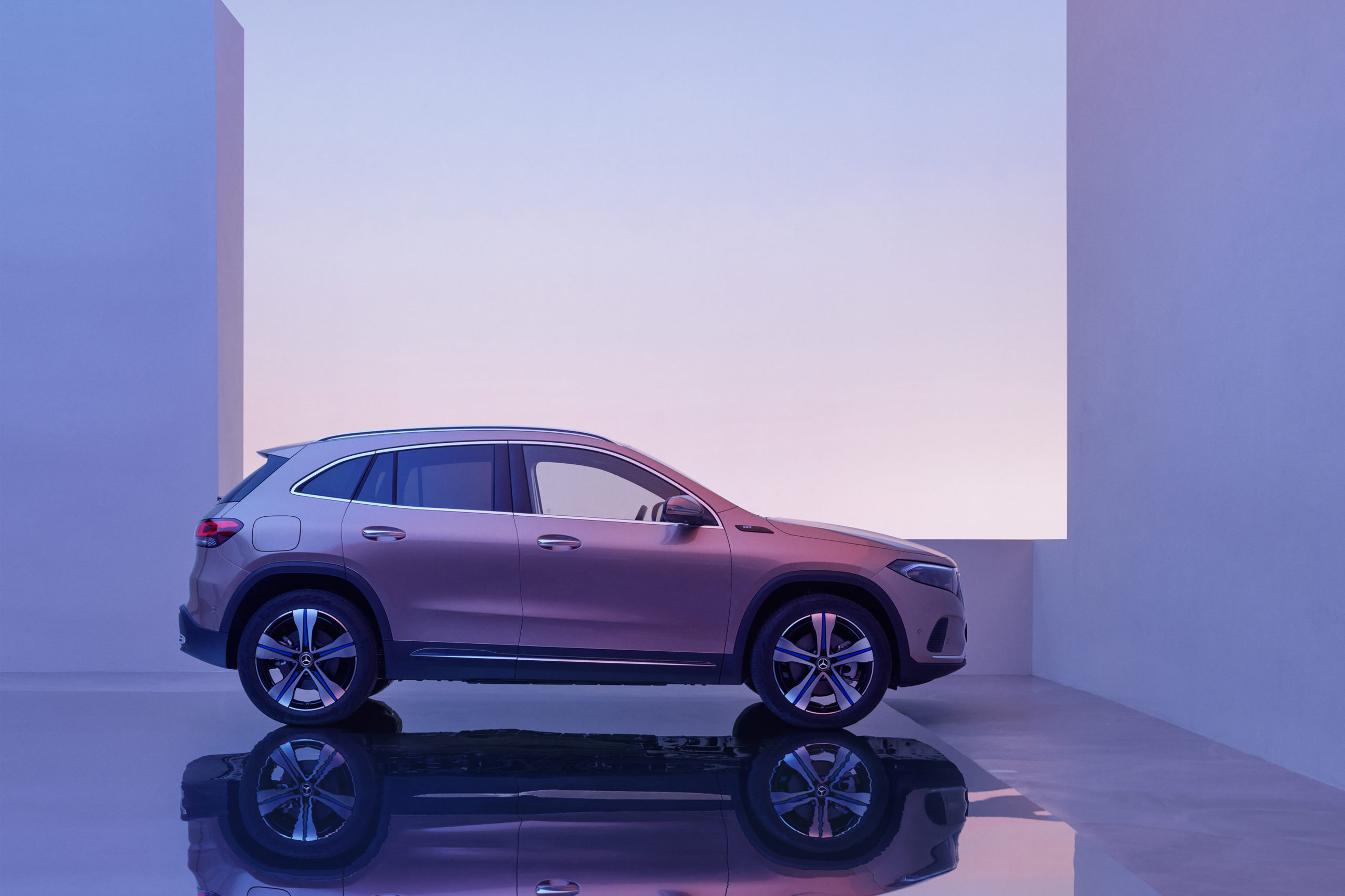
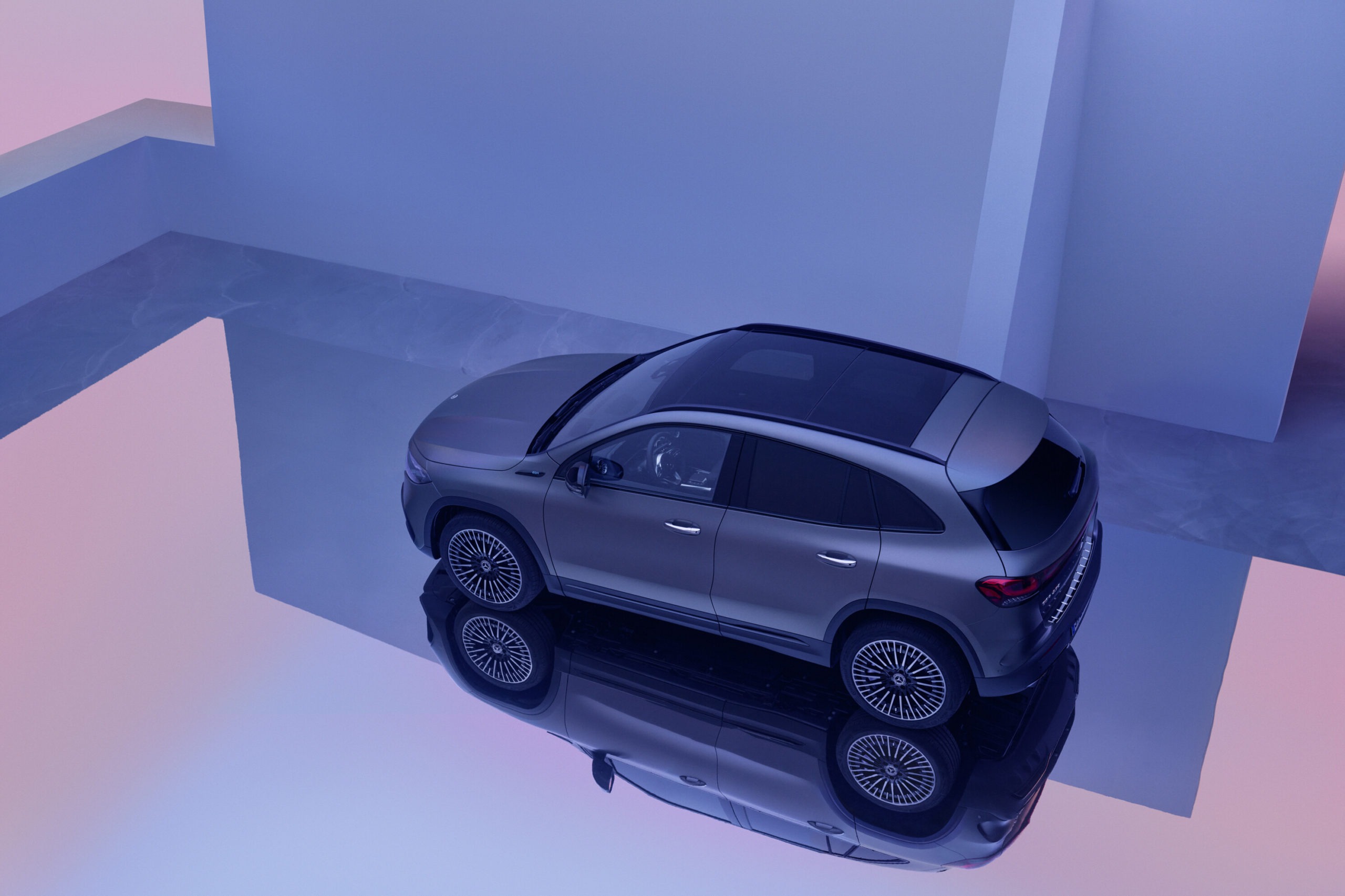
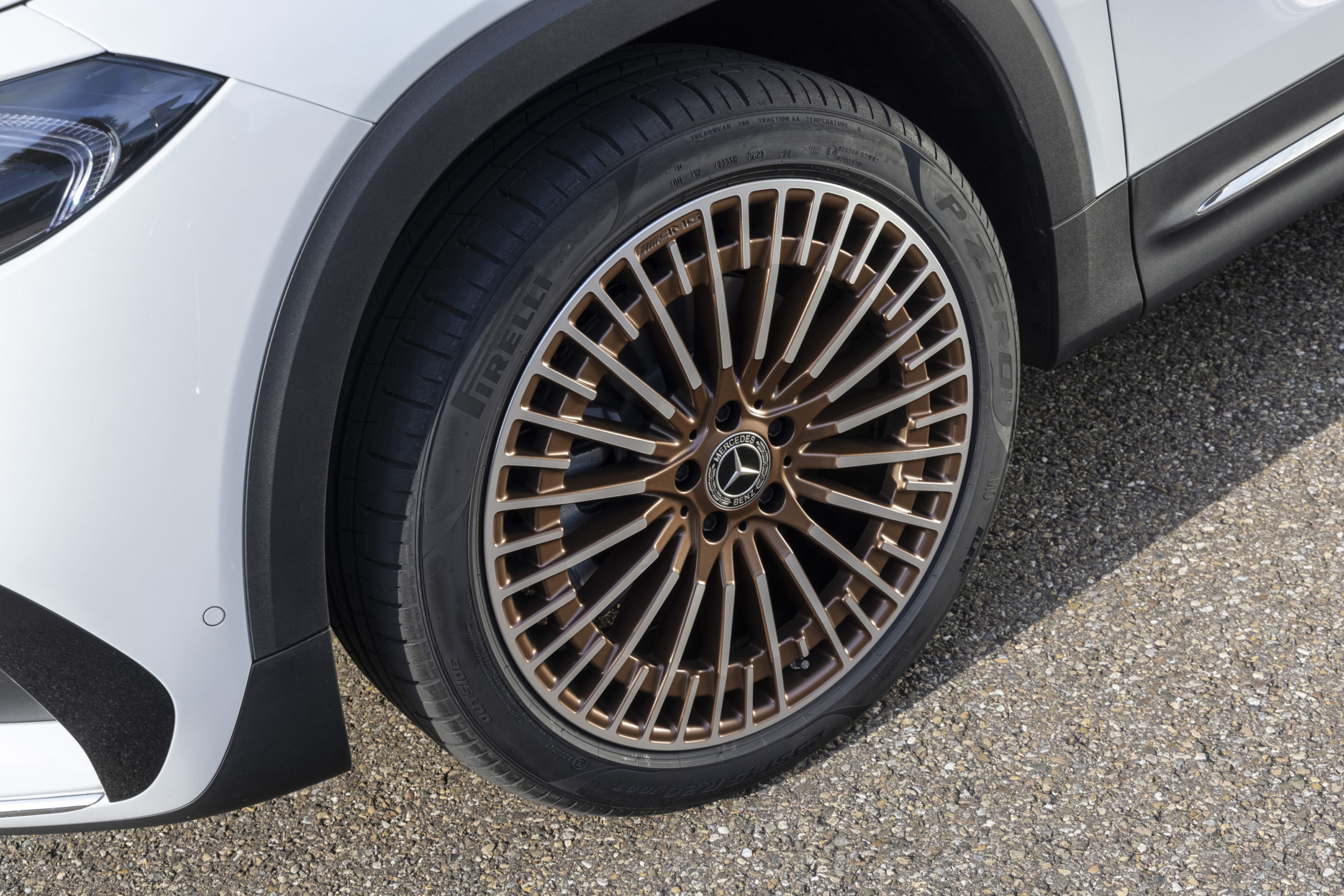
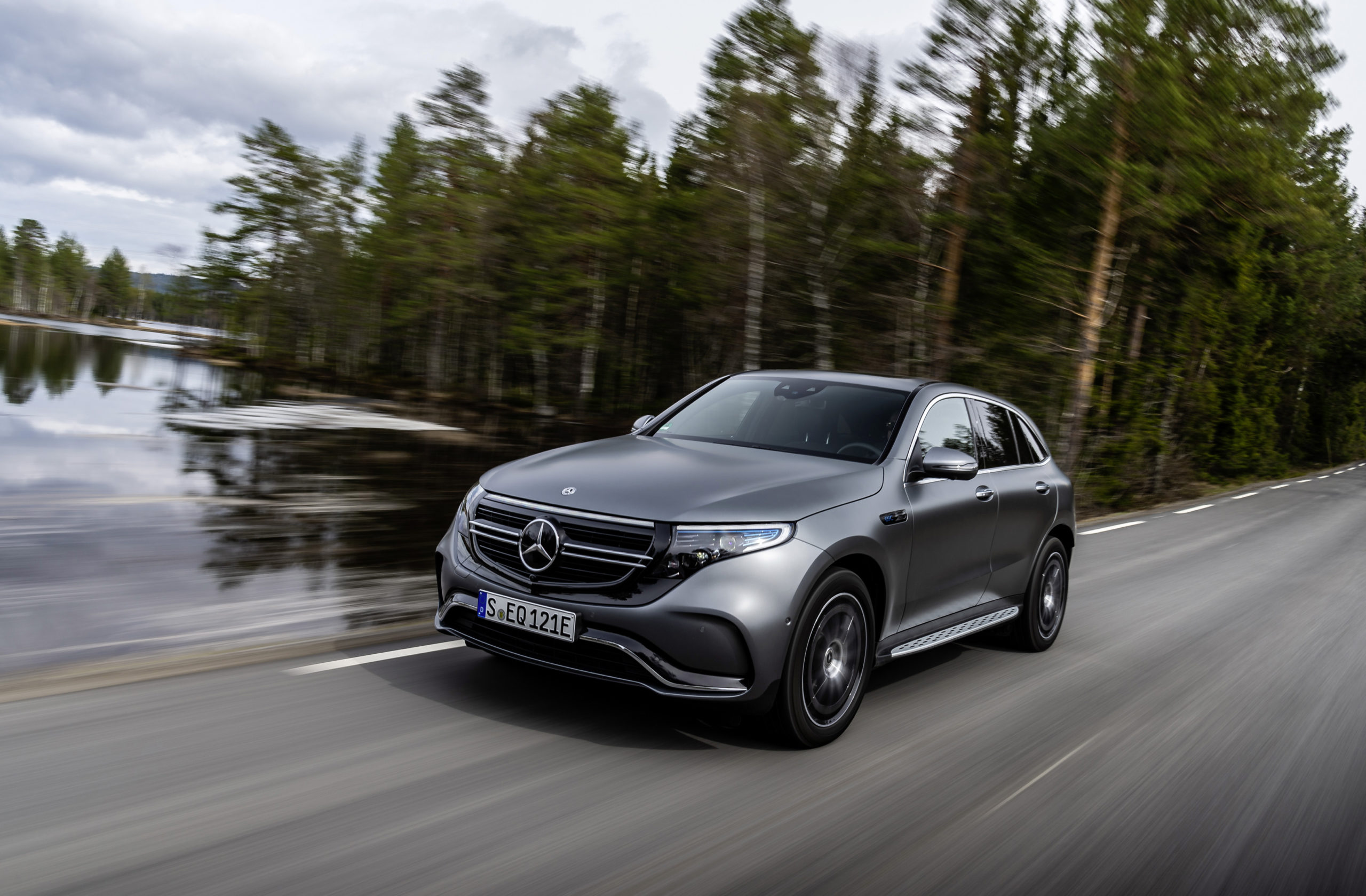
The first ever electric MINI looks like a standard MINI Cooper, with the exception of it being adorned with rather futuristic looking wheels – or heels as our editorial team prefers to call them. The look and feel of these 17-inch MINI Electric Power spoke 2-tone heels give the MINI Cooper SE its unique standing within the urban city environment. Coincidentally the yellow trim on the all new electric MINI matched my green stockings! Clearly green minds think alike.
As much as I am a perfectionist for practicality, I am also a staunch advocate of ‘fashionable’ green mobility. While the new electric MINI does not scream for attention, it does effortlessly exude design elements which set it apart from any other MINI Cooper on the market. These include the embossed MINI Electric logo found on the front grille and on both front fenders. To the rear, the MINI Cooper SE boasts a yellow S which can also be found on the door sills. These small details tastefully differentiate the all new electric MINI from its siblings.
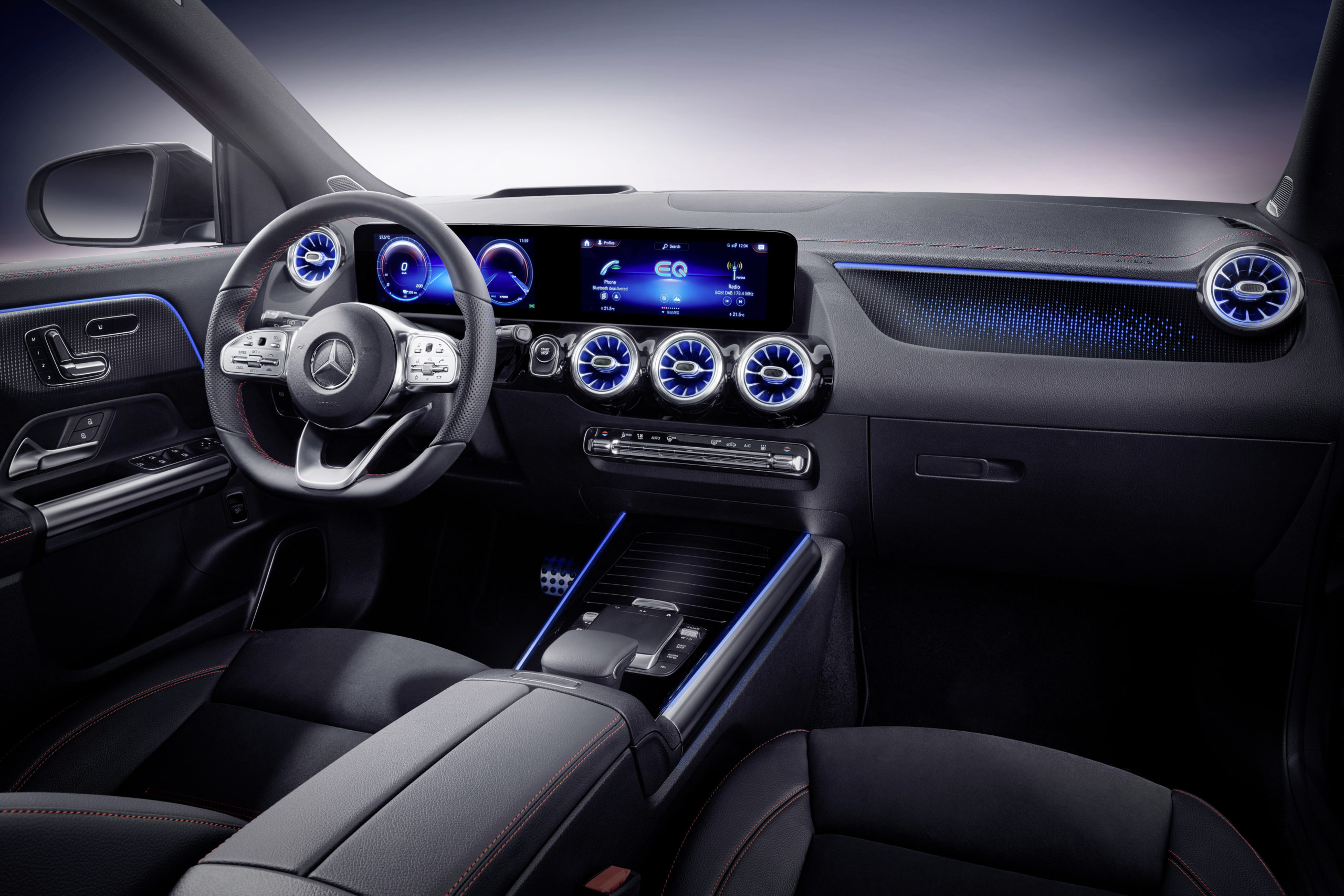
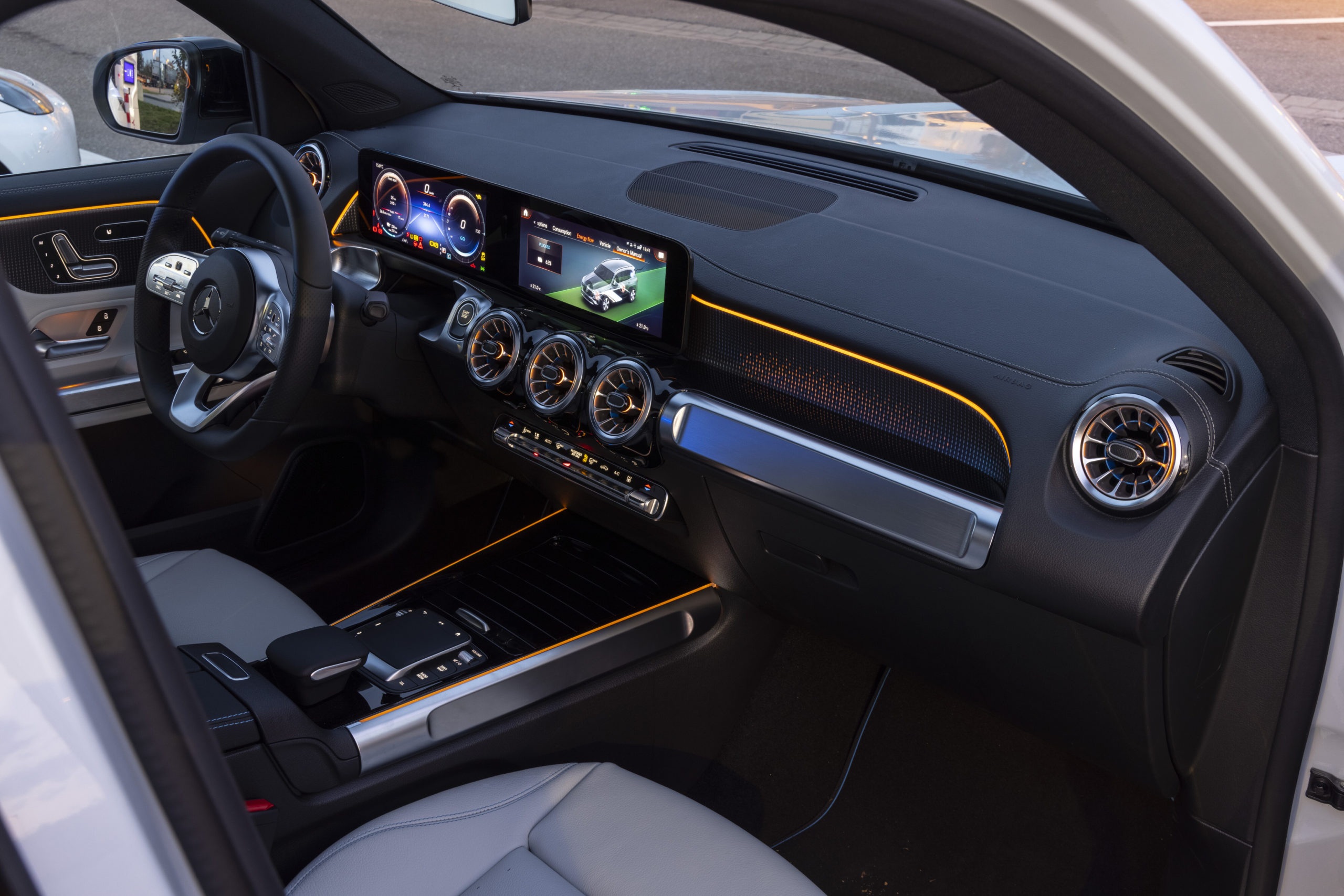
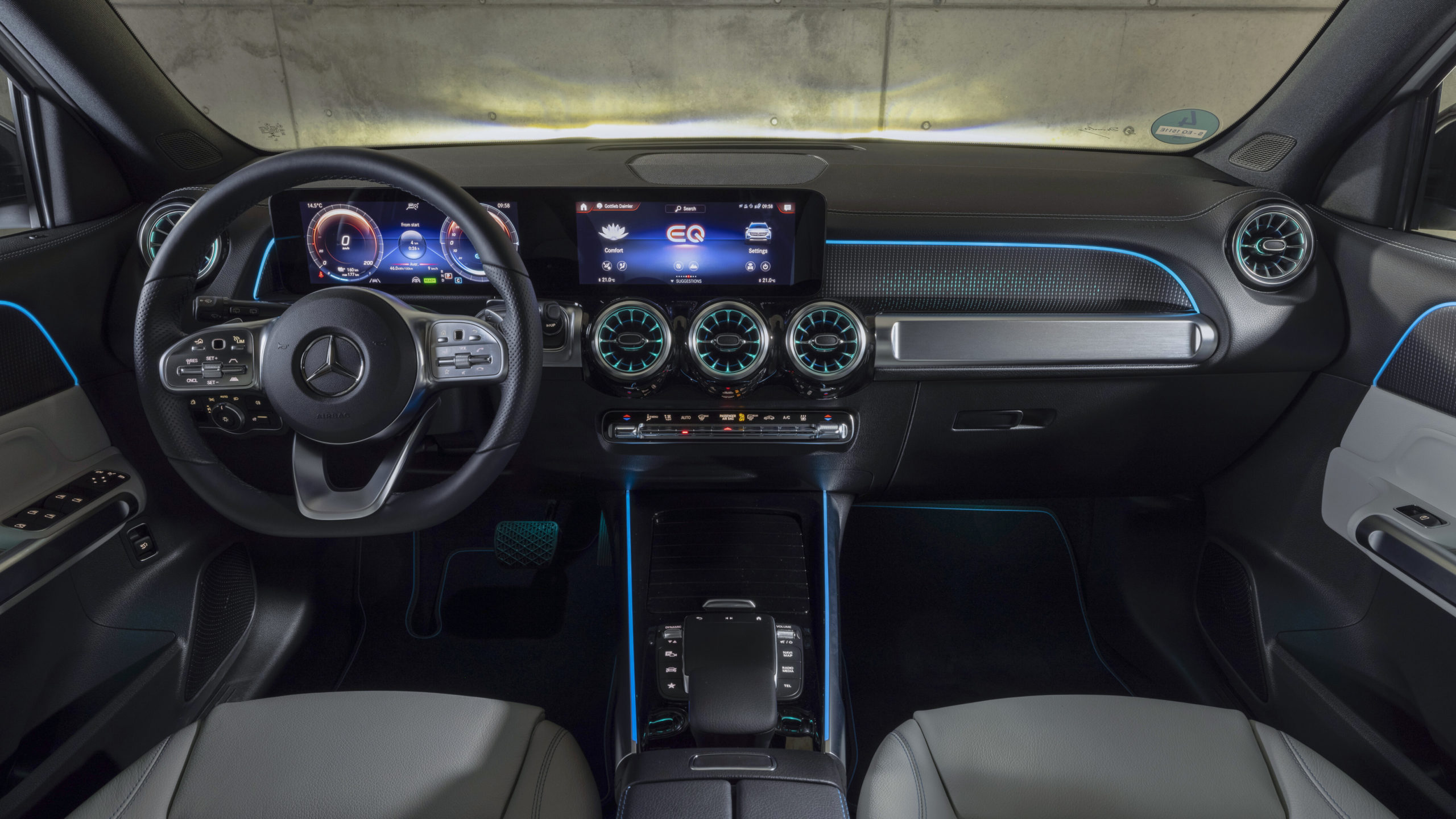
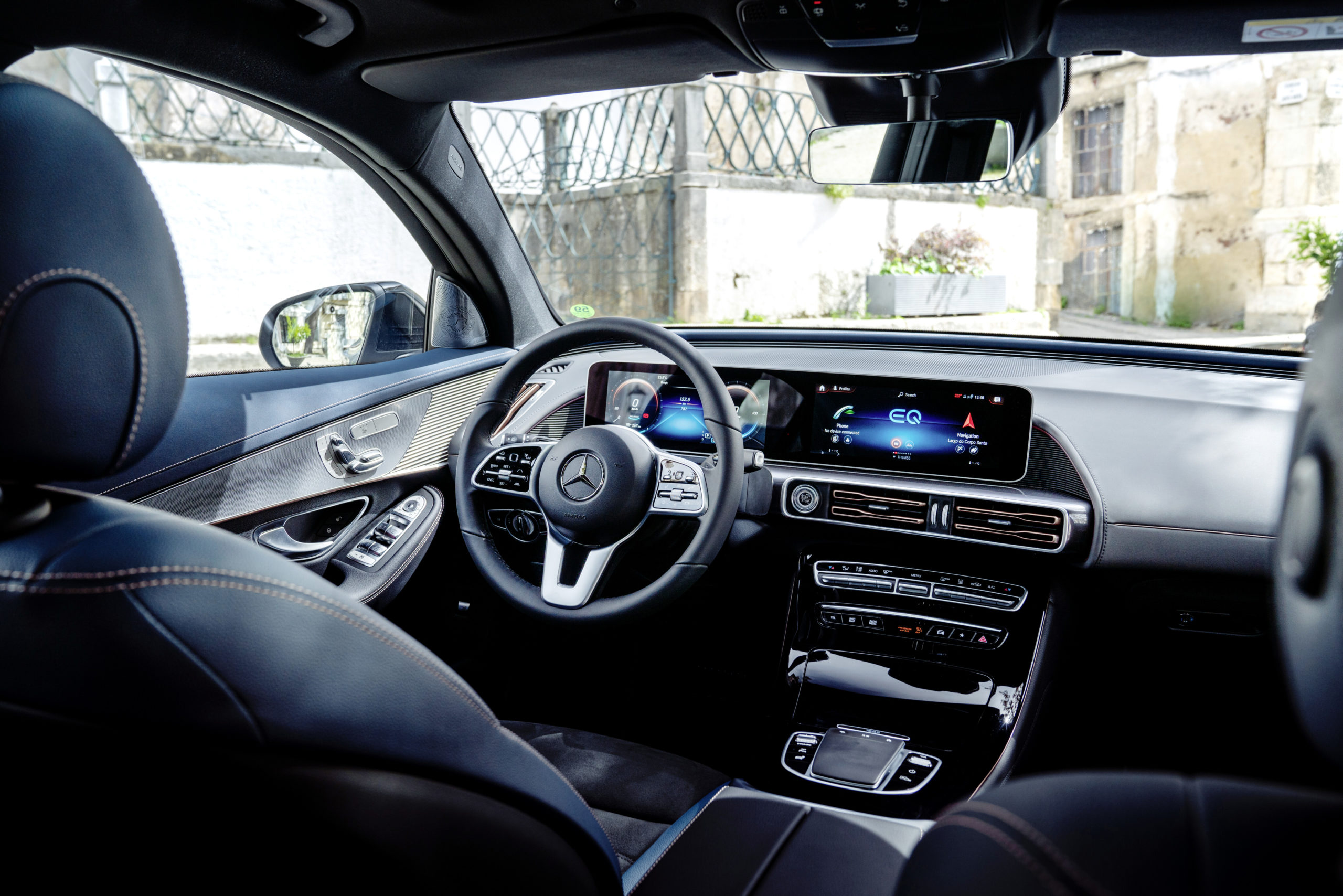
Inside, the all new electric MINI Cooper SE is as spacious as any other. Premium quality materials have been used throughout and give a welcome sense of familiarity to those who know the MINI brand.
I was impressed that the electric MINI has not lost an ounce of all that makes it a fun drive.
– songo didiza, green mobility guru, driving in heels South Africa
The drive
To say I was excited to get behind the wheel of the all new electric MINI would be a gross understatement. It took a lot of effort, but I managed to curb my enthusiasm and remind myself of our publication’s criteria for the Green Mobility Test. These include driver-friendliness, technology, driving range and safety especially when navigating through bustling city traffic.
The MINI ticked all these boxes within the first 30-minutes of my powering it along the highway and within rather tight urban spaces. All the while, the grin on my face was a permanent feature. Not only did I arrive to all my different destinations safely and on time I was impressed that the electric MINI has not lost an ounce of all that makes it a fun drive.
The eery silence of electric cars is one of the global leading safety concerns for both the drivers, pedestrians and other road users.
– SONGO DIDIZA, GREEN MOBILITY GURU, DRIVING IN HEELS SOUTH AFRICA
Instead of a petrol or diesel, the MINI Cooper SE is propelled by a smooth flow of power courtesy of its 135kW motor. This explains how the engineers at MINI have managed to retain the fun factor of the tried, tested and much-loved MINI go-kart feel! It accelerates from standing to 60 km/h in just 3.9 seconds and effortlessly keeps pace with conventionally powered cars.
The eery silence of electric cars is one of the global leading safety concerns for both the drivers, pedestrians and other road users. That said it seems MINI’s engineering team skillfully addressed some of these safety concerns. All components of the electric drive are protected by means of model-specific structural features and that immediately switch off in the event of a collision.
Different driving modes increase the driving fun factor
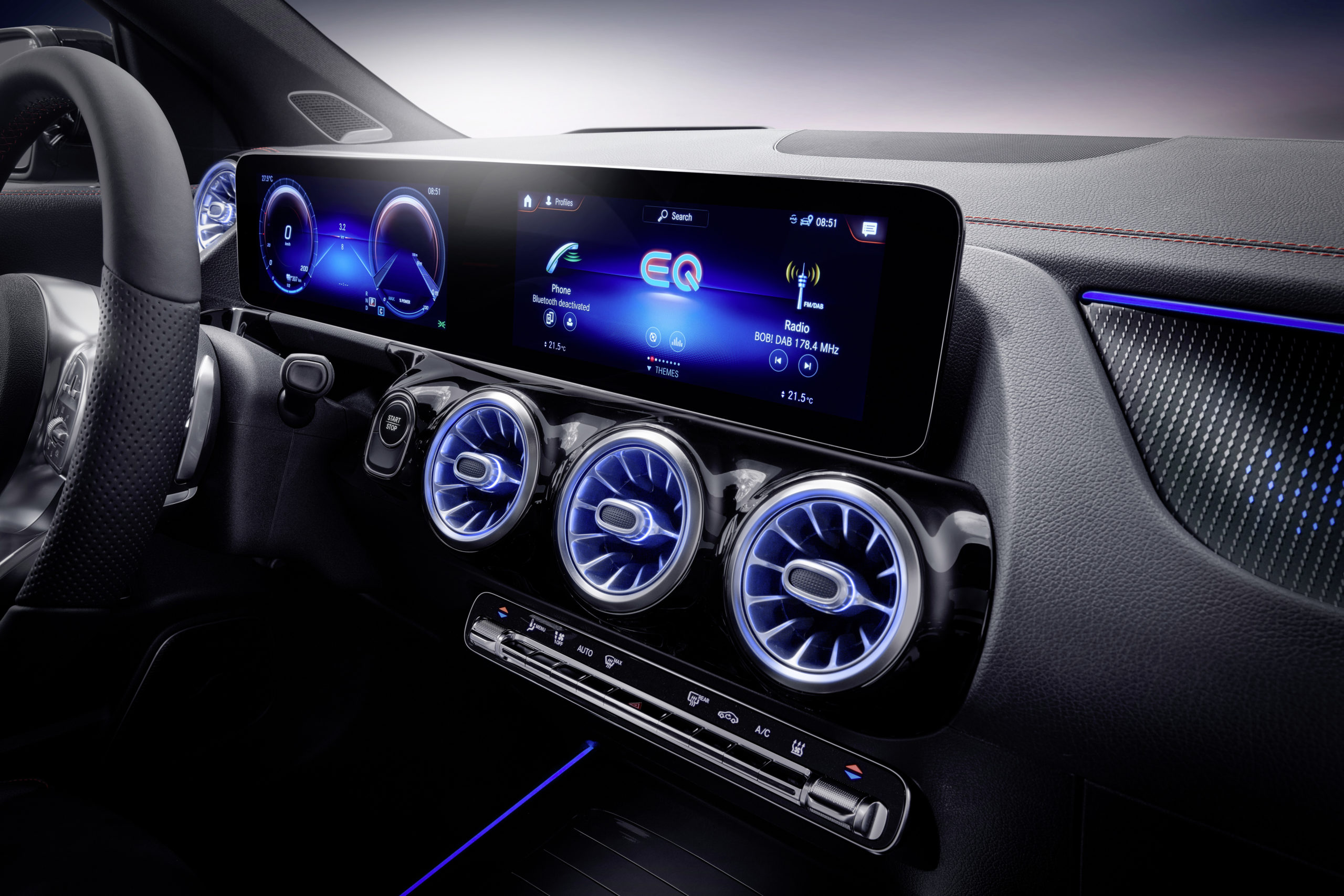
The first purely electrically powered MINI also enables the driver to adapt the vehicle settings to the current situation on the road as well as to their own personal preferences. There are four driving modes to choose from in the electric MINI (MID, Sport, Green and Green+). As I toggled from one mode to the next, I was delighted that the dashboard lit up in different colours, in accordance with which ever mode I had selected. White is for MID, red is for Sport mode and green is for, you guessed it, Green and Green+.
In Green+ one sacrifices features such as air conditioning and seat heating in order to increase the driving range.
– songo didiza
I opted to drive in Green+ mode as this is the most environmentally friendly option. However, when in Green+ one sacrifices features such as air conditioning and seat heating in order to increase the driving range.
MINI’s one pedal drive feature is enabled by BMW’s regenerative braking technology that can be found in all its Battery Electric Vehicles and Plug in Hybrid Vehicles.
MINI eDrive Services were specifically developed for the new all-electric MINI and make electro-mobility particularly easy and convenient
– Hailey Philander, Specialist: Product Communications (BMW i, BMW Motorrad and MINI)
What is Regenerative Braking and how does it work?
Part of the characteristic driving experience in an electrically powered BMW Group model is the so-called one-pedal feeling. In urban traffic in particular, the vehicle perceptibly decelerates as soon as the driver removes their foot from the accelerator. This is called regenerative braking technology.
It is called regenerative because the energy is recaptured in the battery where it can be used again. The motor is directly coupled to the wheels, so when you lift your foot off the pedal, it works like a generator and lets the all-electric MINI slow down more quickly than a fuel-powered car would. You put some power back into your battery every time you come to a stop at the next set of traffic lights. A proper implementation of regenerative braking system extends driving range, improves braking efficiency, reduces brake wear, and improves energy conservation.
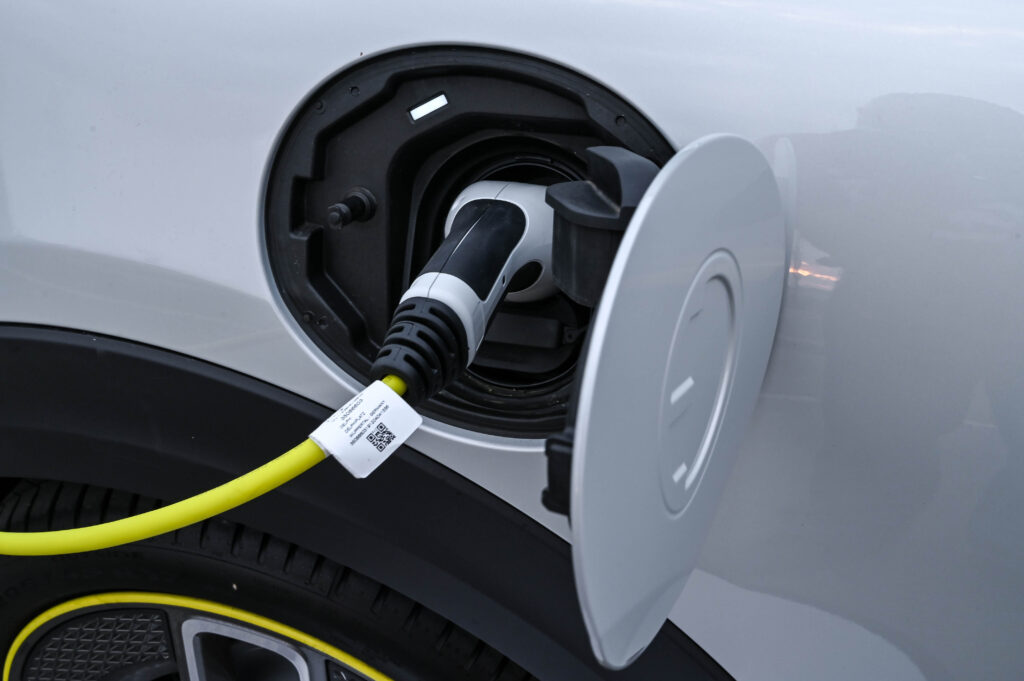
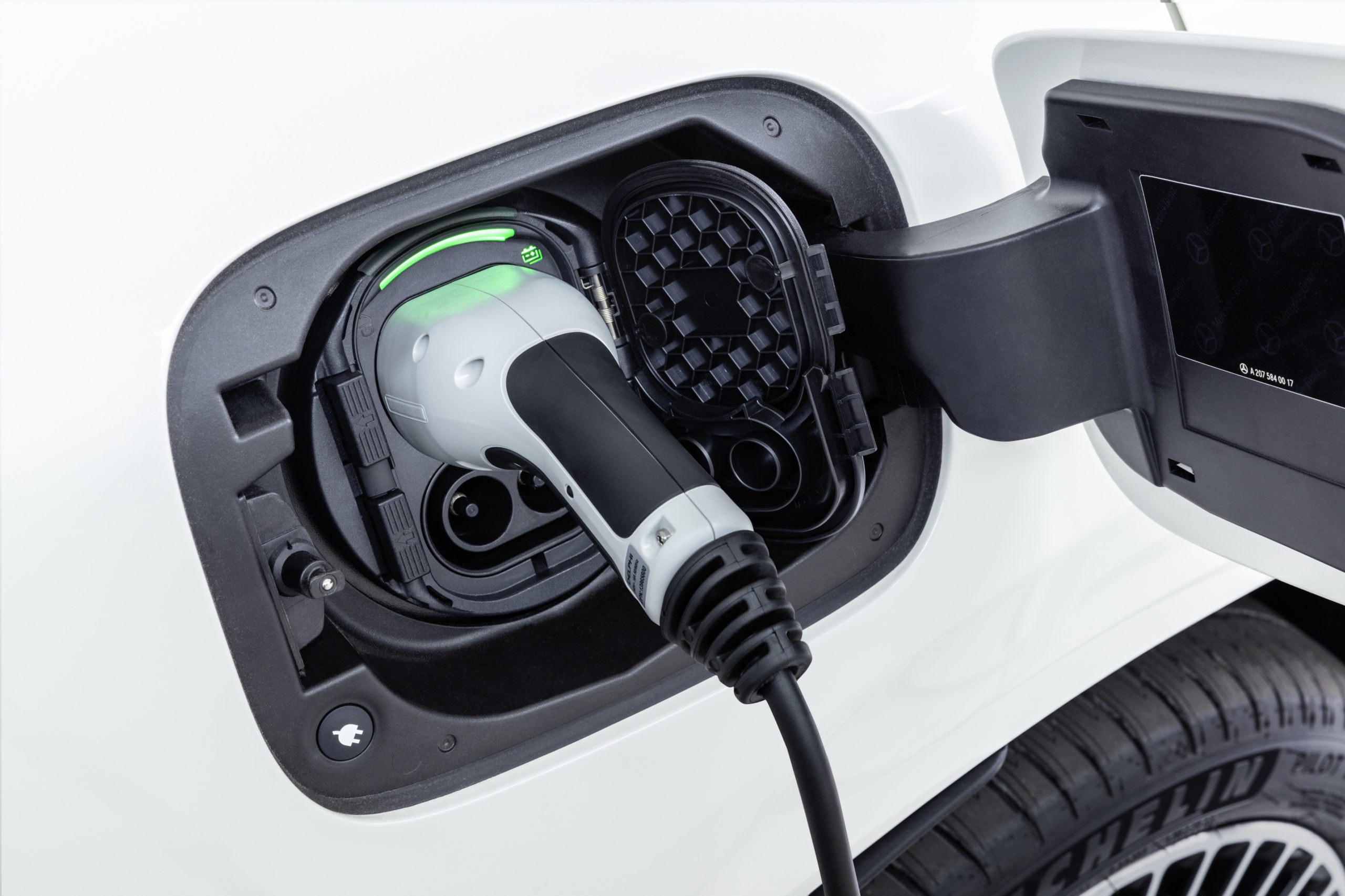
Ease of Charging – how to keep your electric charge while navigating through city effortlessly
South Africa is very much in the early stages of electric mobility compared to its US and European counterparts, however it is a first mover on the African continent.
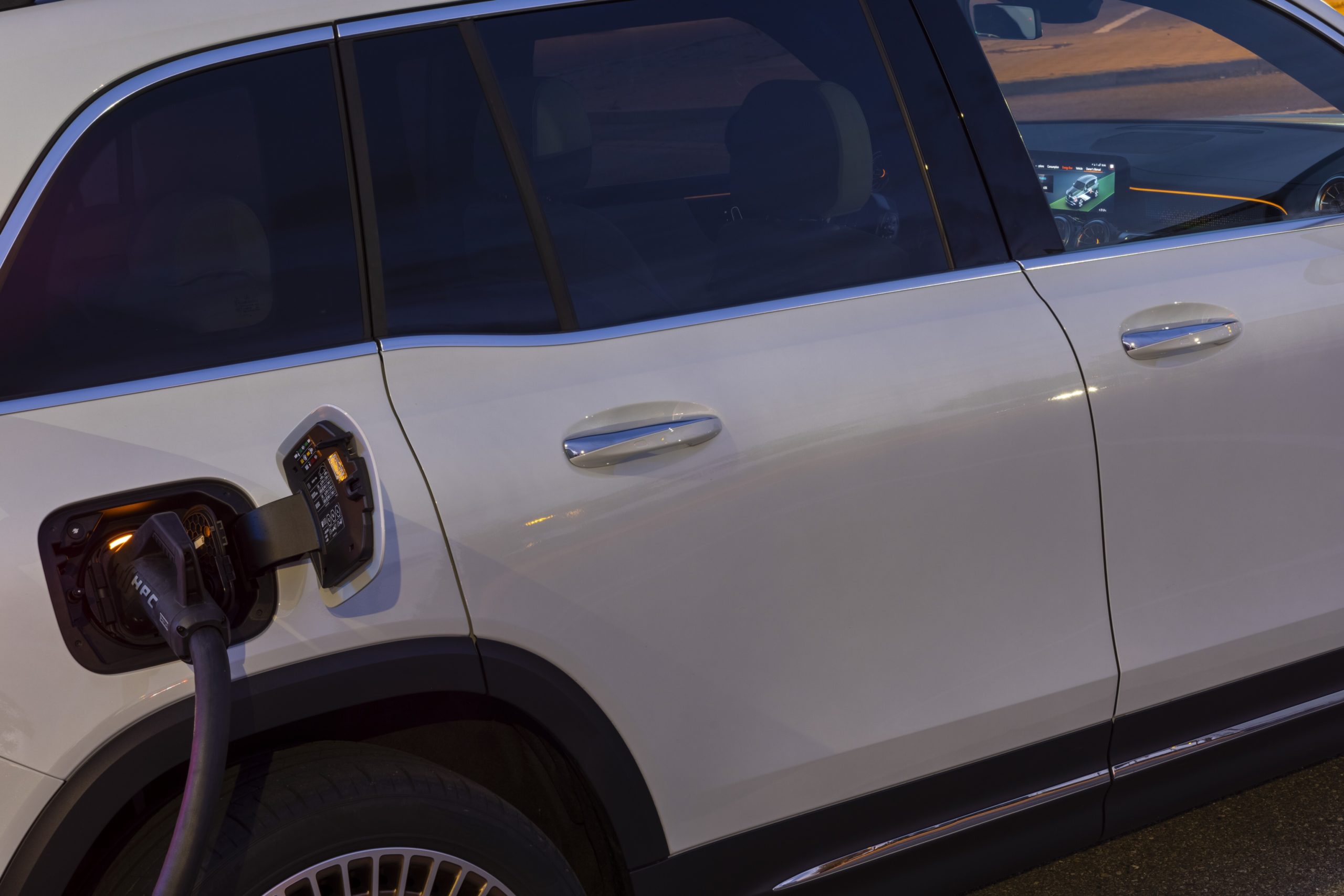
“MINI eDrive Services were specifically developed for the new all-electric MINI and make electro-mobility particularly easy and convenient. For instance, it provides useful details such as available range, charging status and the closest charging station,” Hailey said.
For a city executive, this makes the drive even more practical. The home charging is also a seamless and simple process (unless of course, you are experiencing load-shedding). One does not actually need any complex installation or unit to charge at home. All you have to do is plug into any conventional household power socket – and relax after a long busy day at the office. I can wake up, fully rested in the morning to a ‘full tank’ of 270km driving range to start the day which can be sufficient for a week’s drive of my daily 33km city commute.
For a faster charge MINI recommends a 3-phase 11 kW MINI Wallbox connection will generally give you up to 3-times faster charging time. So, your all-electric MINI can be fully charged within around 3.5 hours. These MINI Wallboxes need to be installed by a qualified electrician.
The MINI navigation system provided me with direct access to all charging stations in the MINI Charging network as well those of the broader BMW charging network since MINI is part of the BMW Group.
Leaping into the new decade we can anticipate greater amount of driving range between the Battery Electric Vehicles, Plug in Hybrid Electric Vehicles in response to changing demands of the African city business executives looking towards making an affordable eco-conscious motoring purchase.
Pros and Cons of purchasing Electric Vehicles in South Africa
Before you rush off to your nearest MINI dealership to buy your favorite go-kart in greenie derivative, be aware that the South African government currently views earth friendly cars as luxury items. As a result, green cars attract an import duty of 25% whereas the duty charged on cars with internal combustion engines is much lower at 18%. This obviously creates a problem for both manufacturers and potential customers.
Presently there aren’t any EVs manufactured locally, even though South Africa is a major car exporter to markets in Great Britain and Europe. These countries are in the process of phasing out internal combustion engines and it is only a matter of time before the South African government finds itself in need of a more sustainable approach towards its efforts to support electric mobility – across the board – if not specifically for export purposes.
The good news though is that the introduction of the carbon tax is a move in the right direction as it acts as an incentive to sway city executives towards zero emission mobility. For this reason, I believe the introduction of an affordable vehicle such as the all new MINI Cooper SE will attract potential customers towards electric mobility.
So, did the Electric MINI pass the Green Mobility Test?
In order to pass the Green Mobility test, the Heels and Horsepower team looks at a number of elements including affordability, drivability and electric mobility features. Overall, the all-electric MINI Cooper SE tested well against our criteria as follows:
- Pricing: Currently, electric vehicles aren’t cheap, but the all-electric MINI Cooper SE comes in at R642 000. This makes it the most affordable electric vehicle in South Africa.
- Drivability: My initial thoughts bordered along the lines that the MINI Cooper SE might be a bit of a snooze fest given that it is a plug in electric vehicle. Thankfully I was wrong. There is absolutely no difference between driving the MINI Cooper SE and any other MINI. None of the MINI fun factors have been compromised in the production of this new greenie.
- Electric mobility features are available in abundance within the new electric MINI, providing the manufacturer with an opportunity to enter a new customer segment – the eco-conscious city executive that is looking for a little bit of everything at the right price!
Final thoughts…
The new MINI Cooper SE is the first model to combine electromobility in the urban setting with the hallmark brand properties of the original in the premium segment of small cars. This gives it an intergenerational edge over its competitors.
Based on these assessments we have confidently given the MINI Cooper SE a very high 8 heels out of 10!